When AI Meets Blockchain: Unlocking the Future of Intelligent Distributed Ledgers
by LCX Team · October 31, 2025
Explore how AI and blockchain work together to enhance data integrity, automation, and transparency. Discover the opportunities, challenges, and future potential of this powerful technological fusion.…
In recent years, two of the most transformative technologies—artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain—have matured in parallel. On one hand, AI systems increasingly analyze vast data sets, drive decision-making, generate content, and automate workflows. On the other hand, blockchain networks offer cryptographically secure, decentralized, and trust-minimized infrastructure for value transfer and data recording. When these two pillars converge, they open possibilities that neither could fully realize alone.
In this article we explore the convergence of AI and blockchain, examine real-world use cases, identify the core advantages and the technical hurdles, and reflect on what the future may hold when intelligent agents operate atop distributed ledgers.
The Convergence: Why AI and Blockchain Are a Natural Pair
AI systems thrive when fed rich, reliable data; they become fragile when the data is tampered with, biased, or poorly recorded. Blockchain technology, with its immutable ledgers, decentralized governance and transparent records, is well positioned to provide a strong foundation for data integrity. Conversely, blockchain networks often suffer from bottlenecks—limited throughput, high latency, and constrained decision-making logic. Embedding AI capabilities into decentralized architectures offers a route to greater automation, smarter contract logic, and predictive services.
In essence, AI brings intelligence to the ledger; blockchain brings trust to the intelligence. By fusing the two, we move toward systems that are autonomous yet auditable, decentralized yet predictive, and automated yet verifiable.
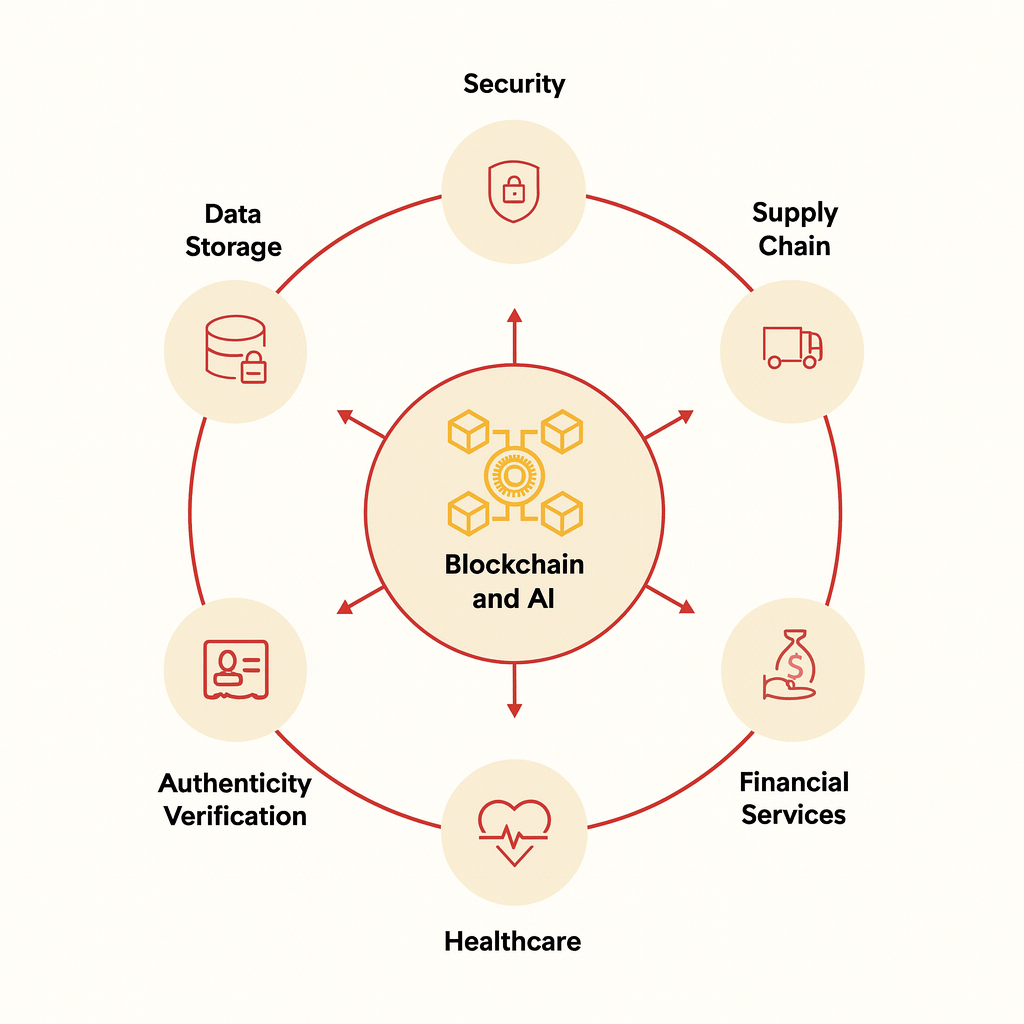
Key Use Cases: Where the Integration Delivers Value
1. Strengthening Security
Combining AI with blockchain enables a secure, defense-in-depth architecture. AI models can detect anomalous behavior or adversarial agents across a network, while blockchain ensures audit trails, tamper-proof logs and decentralized key-management. In this way, the pairing reduces attack surfaces and enhances resilience.
2. Supply Chain & Logistics
In supply-chain contexts AI can analyze demand patterns, forecast disruptions and optimize logistics. Blockchain meanwhile records every movement, transition and event immutably. Together, they enable end-to-end automation: AI triggers smart-contract conditions (such as re-ordering inventory) and blockchain enforces transparency, provenance, and real-time visibility.
3. Authenticity and Media Verification
With generative AI tools becoming increasingly capable, the risk of deep-fakes and manipulated media rises. Blockchain can serve as a ledger of provenance—tracking origin, timestamping changes and establishing ownership—while AI analyzes the content for tampering, patterns and authenticity. The result is a trusted platform for verifying digital media in a world of synthetic generation.
4. Data Analytics & Decentralized Learning
Blockchain networks already generate vast amounts of on-chain data. AI models can mine these data sets to uncover trends, detect inefficiencies and optimize protocol parameters. Further, federated or decentralized learning can be applied: multiple parties train AI models collaboratively while blockchain maintains an immutable record of contributions, updates and model provenance.
5. Financial Services & DeFi
In decentralized finance (DeFi), AI can power automated investment strategies, fraud detection, risk modelling and dynamic fee systems. Blockchain delivers composable finance services, transparent workflows and immutable settlement. The partnership enables smart agents to execute financial operations on-chain with minimal intermediary involvement and auditable logic.
6. Healthcare & Life Sciences
Sensitive and regulated domains like healthcare benefit from this integration. AI requires secure, high-quality data; blockchain ensures reliable records, patient consent management and traceability. Together they can deliver personalized diagnostics, secure data sharing across research institutions and reliable provenance of clinical data.
Advantages: What the Integration Enables
- Data Integrity and Trust: Blockchain assures that the data feeding AI models is tamper-resistant, enhancing confidence in model outcomes.
- Automation at Scale: AI-driven triggers and on-chain smart contracts automate workflows, reducing manual overhead and latency.
- Transparency and Auditability: Blockchain’s ledger enables audit trails of AI decisions, inputs and outcomes, improving accountability.
- New Business Models: Data-markets, compute-markets, tokenized AI services, and decentralized training frameworks become feasible.
- Scalable Intelligence: With blockchain’s decentralized architecture supporting distributed agents, intelligence becomes more global and resilient.
Challenges: What Must Be Addressed
- Interoperability: Integrating AI platforms with blockchain networks involves combining distinct paradigms—data pipelines vs. distributed consensus—and requires standardization.
- Data Privacy vs Transparency: Blockchain’s transparency can clash with privacy-sensitive AI data sets (for instance in healthcare). Balanced design is vital.
- Resource and Latency Constraints: On-chain environments cannot always support heavy AI compute. Off-chain, hybrid or side-chain design may be needed.
- Governance and Incentives: Who governs the AI models? How are incentives aligned for decentralized model training and data contribution?
- Maturity of Tooling and Ecosystem: While individual AI and blockchain stacks are mature, their combined ecosystem remains in early stages; developer tooling, standards and best practices are still emerging.
Looking Ahead: What the Future May Hold
As AI and blockchain increasingly interweave, we may see:
- Smart-contract orchestration by autonomous agents that independently negotiate, execute and settle tasks on-chain.
- Data marketplaces where AI models are trained using tokenised compute and datasets, with contributions tracked on-chain.
- Protocols where AI assists in consensus, verification or dynamic fee adjustment while blockchain ensures decentralised coordination.
- Entire verticals (healthcare, supply-chain, urban infrastructure) re-architected around AI-blockchain synergies rather than layered technology add-ons.
The convergence of intelligent systems and decentralized infrastructure marks more than a technological novelty—it is a shift toward new forms of digital trust, autonomy and value transfer.
Conclusion
The marriage of AI and blockchain is not simply additive; it is multiplicative. Each technology addresses the limitations of the other. AI brings cognitive automation; blockchain brings cryptographic trust. Together, they unlock possibilities for more efficient, transparent, autonomous and secure systems across industries.
For technologists, organizations and investors looking ahead, the question is no longer whether the convergence will matter—it is when and how they will participate. Establishing early competence in this combined domain will prove a differentiator in the emerging landscape of intelligent distributed systems.
